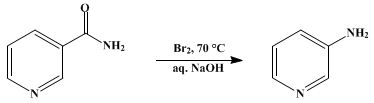 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Pyridin-3-amine | |
| Other names
3-Pyridinamine; 3-Pyridylamine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.658 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H6N2 | |
| Molar mass | 94.117 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | |
| Melting point | 65 °C (149 °F; 338 K) |
| Boiling point | 248 °C (478 °F; 521 K) |
| Soluble | |
| Solubility in alcohol and benzene | Soluble |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 124 °C (255 °F; 397 K) |
| 628 °C (1,162 °F; 901 K) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
3-Aminopyridine is an aminopyridine. It is a colorless solid.[1]
Preparation
3-Aminopyridine is prepared by heating nicotinamide with sodium hypobromite which is in turn prepared in situ by the reaction of sodium hydroxide and bromine at 70 °C.[2]
It can be used in the synthesis of organic ligand 3-pyridylnicotinamide. Troxipide is another synthesis that uses 3-AP.
Toxicity
The acute toxicity is indicated by the LD50 = 178 mg/kg (quail, oral).[1]
References
- 1 2 Shinkichi Shimizu; Nanao Watanabe; Toshiaki Kataoka; Takayuki Shoji; Nobuyuki Abe; Sinji Morishita; Hisao Ichimura (2000). "Pyridine and Pyridine Derivatives". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a22_399. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ↑ Allen, C. F. H.; Wolf, Calvin N. (1950). "3-Aminopyridine". Organic Syntheses. 30: 3. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.030.0003.; Collective Volume, vol. 4, p. 45
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.