 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | heme+O |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C49H58O5N4Fe | |
| Molar mass | 838.854 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
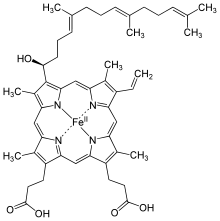
Heme O (or haem O) differs from the closely related heme A by having a methyl group at ring position 8 instead of the formyl group. The isoprenoid chain at position 2 is the same.
Heme O, found in the bacterium Escherichia coli,[1] functions in a similar manner to heme A in mammalian oxygen reduction.
See also
References
- ↑ Myles R. Cheesman; Vasily S. Oganesyan; Nicholas J. Watmough; Clive S. Butler; Andrew J. Thomson (2004). "The Nature of the Exchange Coupling between High-Spin Fe(III) Heme o3 and CuB(II) in Escherichia coli Quinol Oxidase, Cytochrome bo3: MCD and EPR Studies". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126 (13): 4157–4166. doi:10.1021/ja038858m. PMID 15053605.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.