 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
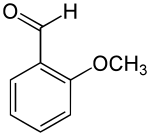
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Methoxybenzaldehyde | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.702 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H8O2 | |
| Molar mass | 136.150 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 1.127 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 34–40 °C (93–104 °F; 307–313 K) |
| Boiling point | 268 °C (514 °F; 541 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 | |
| Warning | |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
2-Methoxybenzaldehyde is an organic compound with the formula CH3OC6H4CHO. It is also commonly referred to as o-anisaldehyde. As a methylated version of salicylaldehyde, the molecule consists of a benzene ring with adjacent formyl and a methoxy groups. It is a colorless solid with a pleasant aroma. The related isomer 4-anisaldehyde is better known, being a commercial flavorant. 2-Anisaldehyde is prepared commercially by formylation of anisole.[1]
References
- ↑ A. J. Sisti (1964). "o-Anisaldehyde". Org. Synth. 44: 4. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.044.0004.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.