 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
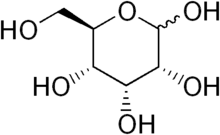
| Preferred IUPAC name
Allose | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2R,3R,4R,5R)-2,3,4,5,6-Pentahydroxyhexanal | |
| Identifiers | |
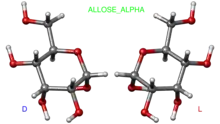
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H12O6 | |
| Molar mass | 180.156 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 128 °C (262 °F; 401 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Allose is an aldohexose sugar. It is a rare monosaccharide that occurs as a 6-O-cinnamyl glycoside in the leaves of the African shrub Protea rubropilosa. Extracts from the fresh-water alga Ochromas malhamensis contain this sugar but of unknown absolute configuration. It is soluble in water and practically insoluble in methanol.
Notes
- ↑ The Merck Index: An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals (11th ed.), Merck, 1989, ISBN 091191028X
References
- Carbohydrates, edited by P.M. Collins, Chapman and Hall, ISBN 0-412-26960-0
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.