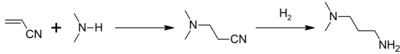 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
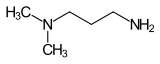
| Preferred IUPAC name
N1,N1-Dimethylpropane-1,3-diamine | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.347 |
| EC Number |
|
| MeSH | 3-dimethylaminopropylamine |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2733 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H14N2 | |
| Molar mass | 102.181 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colourless liquid |
| Odor | fishy, ammoniacal |
| Density | 812 mg mL−1 |
| Boiling point | 132.1 °C; 269.7 °F; 405.2 K |
| log P | −0.211 |
| Vapor pressure | 0.7–2.4 kPa |
Refractive index (nD) |
1.435–1.436 |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C) |
255.7 J K−1 mol−1 |
Std molar entropy (S⦵298) |
323.0 J K−1 mol−1 |
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−76.9–−76.9 kJ mol−1 |
Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
−3.8955–−3.8875 MJ mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 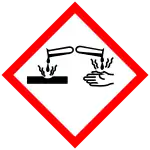  | |
| Danger | |
| H226, H302, H314, H317 | |
| P280, P305+P351+P338, P310 | |
| Flash point | 32 °C (90 °F; 305 K) |
| Explosive limits | 2.3–12.36% |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
|
| Related compounds | |
Related amines |
|
Related compounds |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Dimethylaminopropylamine (DMAPA) is a diamine used in the preparation of some surfactants, such as cocamidopropyl betaine which is an ingredient in many personal care products including soaps, shampoos, and cosmetics. BASF, a major producer, claims that DMAPA-derivatives do not sting the eyes and makes a fine-bubble foam, making it appropriate in shampoos.[1]
Preparation and reactions
DMAPA is commonly produced commercially via the reaction between dimethylamine and acrylonitrile (a Michael reaction) to produce dimethylaminopropionitrile. A subsequent hydrogenation step yields DMAPA:[2]
DMAPA is readily converted to the mustard dimethylaminopropyl-3-chloride, a powerful alkylating agent.[3]
Health effects
Dimethylaminopropylamine is a known skin irritant and its presence as an impurity in cocamidopropyl betaine is thought to be the cause of irritation experienced by some individuals.[4][5]
See also
References
- ↑ "BASF ups capacity at DMAPA plant". Cosmetics Design. 2003-10-28.
- ↑ 3-Aminopropyldimethylamine (PDF). UN Environment.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help) - ↑ Loeliger, P.; Flückiger, E. (1976). "Sulfide Contraction via Alkylative Coupling: 3-Methyl-2,4-Hepthanedione". Organic Syntheses. 55: 127. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.055.0127.
- ↑ Angelini, Gianni; Foti, Caterina; Rigano, Luigi; Vena, Gino A. (February 1995). "3-Dimethylaminopropylamine: a key substance in contact allergy to cocamidopropylbetaine?". Contact Dermatitis. 32 (2): 96–99. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1995.tb00754.x. PMID 7758328. S2CID 20508515.
- ↑ PIGATTO, P (March 1995). "Contact dermatitis to cocamidopropylbetaine is caused by residual amines: Relevance, clinical characteristics, and review of the literature". American Journal of Contact Dermatitis. 6 (1): 13–16. doi:10.1016/1046-199X(95)90062-4.