 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Magnesium dodecanoate, magnesium dilaurate | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.021.571 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
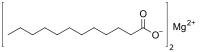
| C 24H 46MgO 4 | |
| Molar mass | 422.9 |
| Melting point | 43.8 °C (110.8 °F; 316.9 K) |
| Boiling point | 296.1 °C (565.0 °F; 569.2 K) |
| Soluble | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Magnesium laurate is a metal-organic compound with the chemical formula C
24H
46MgO
4.[1] The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid (lauric acid).[2]
Physical properties
Soluble in water.[3]
Uses
Magnesium laurate is used in the food industry as a binder, emulsifier, and anticaking agent.[4][5][6]
References
- ↑ "CAS 4040-48-6 Magnesium laurate - Alfa Chemistry". alfa-chemistry.com. Retrieved 2 February 2023.
- ↑ "magnesium laurate". chemsrc.com. Retrieved 2 February 2023.
- ↑ "magnesium laurate, 4040-48-6". thegoodscentscompany.com. Retrieved 2 February 2023.
- ↑ "NCATS Inxight Drugs — MAGNESIUM LAURATE". drugs.ncats.io. Retrieved 2 February 2023.
- ↑ Igoe, Robert S.; Hui, Yiu H. (2001). Dictionary of Food Ingredients. Springer Science + Business Media. p. 85. ISBN 978-0-8342-1952-6. Retrieved 2 February 2023.
- ↑ Burdock, George A. (29 July 2014). Encyclopedia of Food & Color Additives. CRC Press. p. 1625. ISBN 978-1-4987-1108-1. Retrieved 2 February 2023.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.