 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
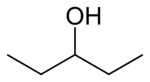
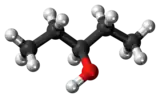
| Preferred IUPAC name
Pentan-3-ol | |
| Other names
3-Pentanol, diethyl carbinol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.662 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H12O | |
| Molar mass | 88.148 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 0.815 g/ml |
| Melting point | −63.68 °C (−82.62 °F; 209.47 K) |
| Boiling point | 115.3 °C (239.5 °F; 388.4 K) |
| 59 g/L | |
| Solubility | soluble in acetone, benzene; very soluble in ethanol, diethyl ether |
| Vapor pressure | 1.10 kPa |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C) |
2.719 J·g−1·K−1 |
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
-368.9 kJ·mol−1 (liquid) -314.9 kJ·mol−1 (gas) |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 41 °C (106 °F; 314 K) |
| 435 °C (815 °F; 708 K) | |
| Explosive limits | 1.2 – 9% |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
3-Pentanol is one of the eight isomers of amyl alcohol. It is found naturally and has a role as a pheromone.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ Lide, David R. (1998), Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.), Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press, pp. 3–454, 5–42, 8–102, 15–23, ISBN 0-8493-0594-2
- ↑ PubChem. "3-Pentanol". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2022-03-25.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.