 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
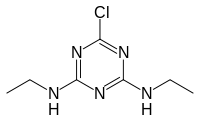
| Preferred IUPAC name
6-Chloro-N2,N4-diethyl-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.124 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H12ClN5 | |
| Molar mass | 201.66 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystalline powder |
| Density | 1.3 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 225–227 °C (437–441 °F; 498–500 K) |
| 5 mg/L | |
| Solubility in other solvents | Soluble in methanol, chloroform, and diethyl ether; slightly soluble in pentane |
| log P | 1.9600 |
| Vapor pressure | 0.000810 mPa at 20 °C |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Simazine is an herbicide of the triazine class. The compound is used to control broad-leaved weeds and annual grasses.
Preparation
Simazine may be prepared from cyanuric chloride and a concentrated solution of ethyl amine (at least 50 percent by number) in water.[1] The reaction is highly exothermic and is therefore best carried out in an ice bath below 10 °C. It is also essential to carry out the synthesis in a fume hood since cyanuric chloride decomposes at high temperatures into hydrogen chloride and hydrogen cyanide, both of which are highly toxic by inhalation.
Properties and uses
Simazine is an off-white crystalline compound which is sparingly soluble in water. It is a member of the triazine-derivative herbicides, and was widely used as a residual non-selective herbicide, but is now banned in European Union states.[2] Like atrazine, a related triazine herbicide, it acts by inhibiting photosynthesis. It remains active in the soil for two to seven months or longer after application.
See also
References
External links
- Simazine, Extoxnet PIP