 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
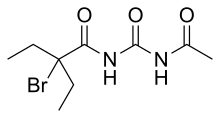
| Preferred IUPAC name
N-(Acetylcarbamoyl)-2-bromo-2-ethylbutanamide | |
| Other names
1-Acetyl-3-(2-bromo-2-ethylbutyryl)urea | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.953 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | acecarbromal |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H15BrN2O3 | |
| Molar mass | 279.134 g·mol−1 |
| Pharmacology | |
| Oral | |
| Legal status |
|
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Acecarbromal (INN) (brand names Sedamyl, Abasin, Carbased, Paxarel, Sedacetyl, numerous others), also known as acetylcarbromal and acetyladalin, is a hypnotic and sedative drug of the ureide (acylurea) group discovered by Bayer in 1917[1] that was formerly marketed in the United States and Europe.[2][3] It is also used in combination with extract of quebracho and vitamin E as a treatment for erectile dysfunction under the brand name Afrodor in Europe.[4][5][6] Acecarbromal is structurally related to the barbiturates, which are basically cyclized ureas.[7] Prolonged use is not recommended as it can cause bromine poisoning.[7]
See also
References
- ↑ DE 327129, "Verfahren zur Darstellung von Derivaten bromacylierter Harnstoffe (Procedures for the preparation of derivatives of bromoacylated urea)", issued 5 October 1920, assigned to Bayer AG
- ↑ Elks J (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 2–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- ↑ Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. January 2000. pp. 4–. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1.
- ↑ Muller NF, Dessing RP, eds. (19 June 1998). European Drug Index: European Drug Registrations, Fourth Edition. CRC Press. pp. 36–. ISBN 978-3-7692-2114-5.
- ↑ Baumbusch F, Papp GK, Kopa ZS (1995). "Treatment for potency problems with Afrodor 2000". Acta Chirurgica Hungarica. 35 (1–2): 87–92. PMID 8659243.
- ↑ Sperling H, Lümmen G, Luboldt HJ, Rübben H (January 1999). "[Secondary erectile dysfunction. Is oral medication in the diagnostic phase indicated?]". Der Urologe. Ausg. A. 38 (1): 56–9. doi:10.1007/s001200050246. PMID 10081103. S2CID 24907635.
- 1 2 Williams DA, Foye WO, Lemke TL (January 2002). Foye's Principles of Medicinal Chemistry. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 380–. ISBN 978-0-683-30737-5.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.