 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
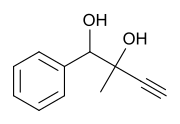
| Formula | C11H12O2 |
| Molar mass | 176.215 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Centalun was developed by Boehringer Ingelheim in 1962[1] and is a psycholeptic drug with hypnotic and sedative effects, via allosteric agonism of the GABAA receptor.[2] It was previously used for sedation in medical procedures such as surgery,[3] orthopedics[4] and gynecology,[5] although it is no longer in clinical use. Despite its history of clinical use, centalun was never incorporated into the CSA and therefore remains unregulated as a drug of abuse.
References
- ↑ BE 618130, "Procédé pour l'obtention d'alkinediols"
- ↑ Janke W, Glathe H (June 1964). "[Experimental Studies on the Psychic Effect of Sedatives Under Normal and Stress Conditions]". Psychologische Forschung (in German). 27: 377–402. doi:10.1007/bf00421338. PMID 14233519. S2CID 144088161.
- ↑ Monecke K (July 1964). "[Pre- and Postoperative Use of Centalun in Surgery]". Deutsches Medizinisches Journal (in German). 15: 470–1. PMID 14238754.
- ↑ Bruckschen E (July 1964). "[Sedative Therapy with Centalun in Orthopedics]". Deutsches Medizinisches Journal (in German). 15: 493–4. PMID 14243120.
- ↑ Gerlach W, Gerlach E (March 1964). "[Experiences with Centalun in Obstetrical and Gynecological Patients]". Medizinische Monatsschrift (in German). 18: 131–3. PMID 14193290.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.