 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Gerodorm |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | cinolazepam |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 90–100% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 3.8 hours[1] |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
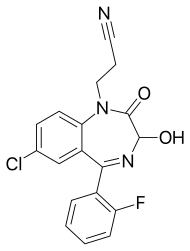
| Formula | C18H13ClFN3O2 |
| Molar mass | 357.8 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
| |
| |
| | |
Cinolazepam[2] (marketed under the brand name Gerodorm)[3] is a drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative. It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, sedative and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. Due to its strong sedative properties, it is primarily used as a hypnotic.
It was patented in 1978 and came into medical use in 1992.[4] Cinolazepam is not approved for sale in the United States or Canada.
References
- ↑ "ZUSAMMENFASSUNG DER MERKMALE DES ARZNEIMITTELS" (Press release). (in Austrian German). Austria: G.L. Pharma GmbH. Bundesamt für Sicherheit im Gesundheitswesen. October 2018. Archived from the original on 2019-01-02. Retrieved 2019-01-02.
- ↑ US Patent 4388313 Novel 3-hydroxy-1,4-benzodiazepine-2-ones and process for the preparation thereof
- ↑ Lannacher Romania (1999). "Gerodorm". Produse Gerot inregistrate in Romania (in Romanian). Archived from the original on 11 October 2006. Retrieved 17 August 2006.
- ↑ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 530. ISBN 9783527607495.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.